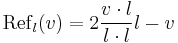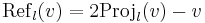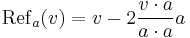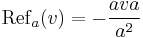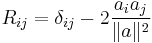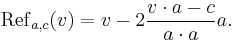Reflection (mathematics)
In mathematics, a reflection (also spelled reflexion) is a mapping from a Euclidean space to itself that is an isometry with a hyperplane as set of fixed points; this set is called the axis (in dimension 2) or plane (in dimension 3) of reflection. The image of a figure by a reflection is its mirror image in the axis or plane of reflection. For example the mirror image of the small Latin letter p for a reflection with respect to a vertical axis would look like q. Its image by reflection in a horizontal axis would look like b. A reflection is an involution: when applied twice in succession, every point returns to its original location, and every geometrical object is restored to its original state.
The term "reflection" is sometimes used for a larger class of mappings from a Euclidean space to itself, namely the non-identity isometries that are involutions. Such isometries have a set of fixed points (the "mirror") that is an affine subspace, but is possibly smaller than a hyperplane. For instance a reflection through a point is an involutive isometry with just one fixed point; the image of the letter p under it would look like a d. This operation is also known as a central inversion (Coxeter 1969, §7.2), and exhibits Euclidean space as a symmetric space. In a Euclidean vector space, the reflection in the point situated at the origin is the same as vector negation. Other examples include reflections in a line in three dimensional space. Typically, however, unqualified use of the term "reflection" means reflection in a hyperplane.
A figure which does not change upon undergoing a reflection is said to have reflectional symmetry.
Contents |
Construction
In plane (or 3-dimensional) geometry, to find the reflection of a point one drops a perpendicular from the point onto the line (plane) used for reflection, and continues it to the same distance on the other side. To find the reflection of a figure, one reflects each point in the figure.
Properties
The matrix for a reflection is orthogonal with determinant -1 and eigenvalues (1, 1, 1, ... 1, -1). The product of two such matrices is a special orthogonal matrix which represents a rotation. Every rotation is the result of reflecting in an even number of reflections in hyperplanes through the origin, and every improper rotation is the result of reflecting in an odd number. Thus reflections generate the orthogonal group, and this result is known as the Cartan–Dieudonné theorem.
Similarly the Euclidean group, which consists of all isometries of Euclidean space, is generated by reflections in affine hyperplanes. In general, a group generated by reflections in affine hyperplanes is known as a reflection group. The finite groups generated in this way are examples of Coxeter groups.
Reflection across a line in the plane
Reflection across a line through the origin in two dimensions can be described by the following formula
Where v denotes the vector being reflected, l denotes any vector in the line being reflected in, and v·l denotes the dot product of v with l. Note the formula above can also be described as
Where the reflection of line l on a is equal to 2 times the projection of v on line l minus v. Reflections in a line have the eigenvalues of 1, and −1.
Reflection through a hyperplane in n dimensions
Given a vector a in Euclidean space Rn, the formula for the reflection in the hyperplane through the origin, orthogonal to a, is given by
where v·a denotes the dot product of v with a. Note that the second term in the above equation is just twice the vector projection of v onto a. One can easily check that
- Refa(v) = − v, if v is parallel to a, and
- Refa(v) = v, if v is perpendicular to a.
Using the geometric product the formula is a little simpler
Since these reflections are isometries of Euclidean space fixing the origin, they may be represented by orthogonal matrices. The orthogonal matrix corresponding to the above reflection is the matrix whose entries are
where δij is the Kronecker delta.
The formula for the reflection in the affine hyperplane 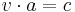 not through the origin is
not through the origin is
See also
- Coordinate rotations and reflections
- Householder transformation
- Inversive geometry
- Point reflection
- Plane of rotation
- Reflection mapping
- Reflection group
References
- Coxeter, Harold Scott MacDonald (1969), Introduction to Geometry (2nd ed.), New York: John Wiley & Sons, ISBN 978-0-471-50458-0, MR123930
- Popov, V.L. (2001), "Reflection", in Hazewinkel, Michiel, Encyclopedia of Mathematics, Springer, ISBN 978-1556080104, http://www.encyclopediaofmath.org/index.php?title=R/r080510
- Weisstein, Eric W., "Reflection" from MathWorld.
External links
- Reflection in Line at cut-the-knot
- Understanding 2D Reflection and Understanding 3D Reflection by Roger Germundsson, The Wolfram Demonstrations Project.